虚拟Dom和Diff算法
大约 4 分钟
""
什么是虚拟DOM和diff
snabbdom
原意:速度
是著名的虚拟DOM,是diff算法的鼻祖,Vue借鉴了snabbdom
环境
- 安装:
npm i -S snabbdom
node_modules中,build目录下,是JS源代码,src目录下,是TS源代码
- 安装webpack
npm i -D webpack webpack-cli webpack-dev-server
创建
/src/index.js文件import { init, classModule, propsModule, styleModule, eventListenersModule, h, } from "snabbdom"; const patch = init([ // Init patch function with chosen modules classModule, // makes it easy to toggle classes propsModule, // for setting properties on DOM elements styleModule, // handles styling on elements with support for animations eventListenersModule, // attaches event listeners ]); const container = document.getElementById("container"); const vnode = h("div#container.two.classes", { on: { click: ((function () { })) } }, [ h("span", { style: { fontWeight: "bold" } }, "This is bold"), " and this is just normal text", h("a", { props: { href: "/foo" } }, "I'll take you places!"), ]); // Patch into empty DOM element – this modifies the DOM as a side effect patch(container, vnode); const newVnode = h( "div#container.two.classes", { on: { click: function () { } } }, [ h( "span", { style: { fontWeight: "normal", fontStyle: "italic" } }, "This is now italic type" ), " and this is still just normal text", h("a", { props: { href: "/bar" } }, "I'll take you places!"), ] ); // Second `patch` invocation patch(vnode, newVnode); // Snabbdom efficiently updates the old view to the new state创建
webpack.config.js文件const path = require('path') module.exports={ //入口 entry:'./src/index.js',//相对路径 //输出 output:{ //文件名 filename:'bundle.js' }, //模式 mode:'development', devServer: { //静态资源根目录 static: { directory: path.join(__dirname, 'www'), }, //不压缩 compress: false, //端口号 port: 9000, //虚拟打包路径 // publicPath:"/xuni/" }, }修改
package.json"scripts": { "dev":"webpack-dev-server" },创建
/www/index.html<body> <div id="container"></div> <script src="/bundle.js"></script> </body>启动
npm run dev
h函数
虚拟DOM如何被渲染成函数产生
h函数用来产生虚拟节点(vnode)
h函数
如:
h('a',{props:{href:'http://blog.erickiku.xyz'}},'我的博客')
将得到虚拟节点:
{
"sel":"a",
"data":{
props:{
href:'http://blog.erickiku.xyz'
}
},
"text":'我的博客'
}
真正的DOM节点
<a href="http://blog.erickiku.xyz">我的博客</a>
h函数的其他写法:
h('a','我的博客') //没有属性,就可以不写中间的对象
let vnode2 = h('ul',[ //可以嵌套使用h函数
h('li','汉堡包'),
h('li','热狗'),
h('li','鸡翅'),
h('li','可乐'),
])
虚拟节点的属性
{
children:undefined //是否有后代元素
data:{} //元素上的属性,href等
elm:undefined //是否上树
key:undefined //节点的唯一标识
sel:'a' //选择器
text:"我的博客" //元素中的文字
}
手写简易版h函数
import vnode from "./vnode";
/*
*@Author: EricKiku
*@Date: 2022-10-17 16:38:22
*@Description: 手写简易版h函数
*/
/*
完整版可以接收任意参数,简易版需要三个参数
形式1:h('div',{},"文字")
形式2:h('div',{},[])
形式3:h('div',{},h())
*/
export default function (sel,data,c) {
if (arguments.length != 3) {
throw new Error('需要三个参数')
}
if (typeof c === 'string' || typeof c === 'number') {
return vnode(sel,data,undefined,c,undefined)
}else if(Array.isArray(c)){
//说明c是一个数组,说明该dom元素有后代节点
let children =[]
//遍历c
for (let i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
//检查数组中的所有项,是不是一个h函数返回的对象,在检查时,就会自动调用数组中的h函数,变相的递归
if (typeof c != 'object' && !(c[i].hasOwnProperty('sel'))) {
throw new Error('数组中有项不是h函数')
}
children.push(c[i])
}
//循环结束,返回对象
return vnode(sel,data,children,undefined,undefined)
}else if(typeof c === 'object' && c.hasOwnProperty('sel')){
//说明第三个参数是h函数
let children = [c]
return vnode(sel,data,children,undefined,undefined)
}else{
throw new Error('传入的第三个参数类型不正确')
}
}
vnode.js
//函数功能很简单,把传入的参数组成对象返回
export default function (sel,data,children,text,elm) {
return {
sel,data,children,text,elm
}
}
index.js
import h from './mySnabbdom/h'
let retult = h('div',{},[
h('p',{},'erickiku'),
h('p',{},'erickiku2'),
h('p',{}, h('span',{},'2022')),
])
console.log(retult);
diff
diff算法
diff
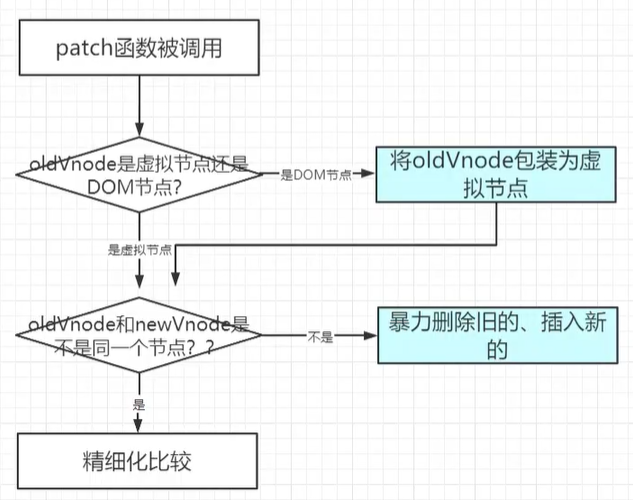
最小量更新,key很重要,只有同一个虚拟节点,才会进行过精细比较,进行最小量更新,否则就是直接删除,再插入新DOM
如何定义同一个虚拟节点:
选择器相同且key相同只进行同层比较,即使是同一个虚拟节点,但是跨层了,也是删除再插入,不会diff
patch函数
patch:修补的意思。旨在对DOM最小量更新
patch函数流程图
手写patch函数
问题3
虚拟DOM如果通过diff变为真正的DOM的
