MyBatis-Plus
""
MyBatis-Plus

快速创建
1 数据库表
现有一张 User 表,其表结构如下:
| id | name | age | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jone | 18 | test1@baomidou.com |
| 2 | Jack | 20 | test2@baomidou.com |
| 3 | Tom | 28 | test3@baomidou.com |
| 4 | Sandy | 21 | test4@baomidou.com |
| 5 | Billie | 24 | test5@baomidou.com |
其对应的数据库 Schema 脚本如下:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
其对应的数据库 Data 脚本如下:
DELETE FROM user;
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');
2 导入依赖
<dependency>
<!--数据库驱动-->
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
尽量不要同时导入mybatis和mybatis-plus
3.连接数据库
application.properties
连接本地数据库:localhost:3306--MySQL8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
连接服务器数据库:39.98.110.164:3306--MySQL5
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
4.创建接口
mybatis-plus不需要service层,dao层和dao实现类,只需要pojo(模型层)和mapper(持久层)
pojo-模型层
使用Lombok自动填充方法
pojo层类名必须和表名一致
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
mapper接口
继承BaseMapper<>,其中参数是泛型,是表类型
//在对应的Mapper上面实现基本的接口 BaseMapper
@Repository //代表持久层
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
// 所有的CRUD操作都已经编写完成
}
5.编写测试类
1.Autowired自动注入userMapper前提是,必须在Springboot启动文件上添加扫描注解
//扫描mapper文件夹
@MapperScan("com.kuang.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
BaseMapper中默认的查询所有有一个条件参数,写null,表示没有条件,查询所有
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisPlusApplicationTests {
//继承BaseMapper,所有的方法都来自父类,也可以编写扩展方法
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//参数是一个Wapper,条件构造器,先使用null
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
配置日志
基础配置,在控制台输出,有规则的日志,其他日志格式的需要导入依赖
#配置日志
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
CRUD扩展
1.insert
只需要在userMapper中的insert方法中传入一个user对象参数,即可插入数据
数据库插入的id的默认值为:全局的唯一id
@Test
public void userInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setName="EricKIku";
user.setAge="20";
user.setEmail="2966678301@qq.com";
userMapper.insert(user);
}
主键生成策略
分布式系统唯一id生成:
https://www.cnblogs.com/haoxinyue/p/5208136.html
在pojo的user中的id字段添加注解
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO),设置主键以什么增长type = IdType.ID_WORKER 默认,全局id
type = IdType.AUTO 自增 要求:数据库的对应字段必须是自增的
type = IdType.NONE 不使用操作
type = IdType.INPUT 手动输入
type = IdType.UUID 全局唯一id
type = IdType.ID_WORKER_STR id_WORKER的字符串截取表示法
雪花算法:
snowflake是Twitter开源的分布式ID生成算法,结果是一个long型的ID。其核心思想是:使用41bit作为毫秒数,10bit作为机器的ID(5个bit是数据中心,5个bit的机器ID),12bit作为毫秒内的流水号(意味着每个节点在每毫秒可以产生 4096 个 ID),最后还有一个符号位,永远是0。几乎可以保证该id全球唯一
2.update
updateById的参数是一个user对象,不是id值
会自动拼接动态sql,无须按照顺序
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(7L);
user.setName("小雨子");
user.setAge(20);
user.setEmail("xiaoxiangzi@gmail.com");
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
3.自动填充
创建时间、修改时间,都需要自动填充,不能手动填写
方式一:数据库级别(尽量不要使用此方法)
插入两个字段create_time和update_time,在默认列填写:CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,默认当前时间
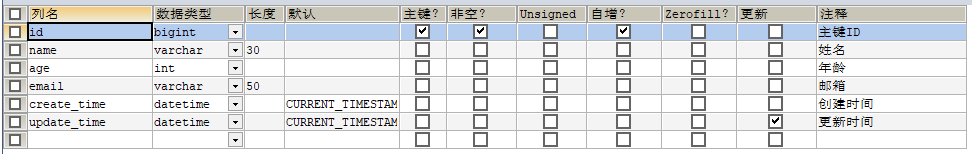
测试插入方法:
更新pojo实体类
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
方式二:代码级别
不使用数据库方法,没有CURRENT_TIMESTAMP默认值,和自动更新
仅仅添加两个字段,字段类型是datetime,更新实体类user
在实体类字段属性上增加注解
@TableField(fill=FieldFill.INSERT)是非主键字段的注解,INSERT表示创建数据时有效,INSERT_UPDATE表示创建和更新时有效,这两个字段无法手动修改
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
编写一个处理器来处理注解
创建一个handle>MyMetaObjectHandler类
使MyMetaObjectHandler实现接口MetaObjectHandler,再实现接口的方法
this.setFieldValByName("createTime",new Date(),metaObject);
第一个参数是:想要改变哪个字段
第二个参数是:为该字段填充什么值
第三个参数是:实现接口方法的参数
@Slf4j
@Component //把该处理器加到IOC容器中
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
//插入时的填充策略
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
this.setFieldValByName("createTime",new Date(),metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
//更新时的填充策略
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}
在创建或更新记录时,这两个字段也会自动填充。
4.select
单个id查询
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println(user);
}
多个id查询
@Test //测试批量查询
public void testSelectByBatchId(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
for(User user:users){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
条件查询
map集合中有多少个元素,就会在where后拼接多少个and
如下:SELECT *l WHERE name = ? AND age = ?
@Test
public void testSelectByBatchIds(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","小雨子");
map.put("age","21");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
for(User user:users){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
分页查询
1.使用limit分页 2.使用pageHelper分页 3.MybatisPlus内置分页
使用MyBatisPlus的分页插件
1.配置拦截器
@MapperScan("com.kuang.mapper")
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Configuration
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.H2));
return interceptor;
}
}
2.编写分页查询
page对象参数: 参数一:当前是第几页 参数二:页面显示几条数据
selectPage参数: 1.分页格式 2.queryWrapper高级查询
page还可以获取总记录个数,是否有上一页,是否有下一页
@Test
public void testPage(){
Page<User> page = new Page<>(2,5);
userMapper.selectPage(page,null);
page.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
5.delete
userMapper.delete() 根据实体删除
userMapper.deleteById() 根据id删除
userMapper.deleteBatchIds() 根据id批量删除
userMapper.deleteByMap() 根据map条件删除
@Test //根据id删除
public void testDeleteById(){
int i = userMapper.deleteById(2L);
System.out.println(i);
}
@Test //根据id批量删除
public void testDeleteBatchIds(){
int i = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
System.out.println(i);
}
@Test //根据map条件删除
public void testDeleteMap(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","zhangsan");
int i = userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
System.out.println(i);
}
逻辑删除
未被真正的删除,只是使记录无效
1.增加一个字段deleted,默认值0
2.实体类中添加字段
@TableLogic //逻辑删除
private int deleted;
3.配置
配置逻辑删除,之后删除的操作将改为修改,将deleted字段修改为1,代表已删除,查询时自动拼接 AND DELETED=0,被逻辑删除的字段查询不到
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-field: flag
logic-delete-value: 1 # 逻辑已删除值(默认为 1)
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 逻辑未删除值(默认为 0)
乐观锁
乐观锁:认为操作数据库时,不会出现问题,不会同时操作数据,如果在修改时发现有操作了,就会再次更新值测试。
悲观锁:认为总是会出现问题,会在操作数据时上锁,执行完毕之后才会释放锁
乐观锁
当要更新一条记录的时候,希望这条记录没有被别人更新 乐观锁实现方式:
- 取出记录时,获取当前version
- 更新时,带上这个version
- 执行更新时, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion
- 如果version不对,就更新失败
1.给数据库中新增一个version字段

2.更新实体类
@Version //乐观锁version注解
private int version;
3.注册组件
config>MyBatisPlusConfig
扫描mapper文件夹的注解也写在这里
//扫描mapper文件夹
@MapperScan("com.kuang.mapper")
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Configuration
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
mybatisPlusInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
return mybatisPlusInterceptor;
}
}
4.测试
使用乐观锁,成功修改
数据被修改了
// 测试乐观锁成功
@Test
public void testLeGuanSuo(){
//查询用户
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
//修改用户
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setEmail("xingyizhe@qq.com");
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
使用乐观锁,修改失败
数据变为第二个修改的数据,第一个失败
// 测试乐观锁失败
@Test
public void testLeGuanSuo2(){
//模拟线程一
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user.setName("zhangsan3333");
user.setEmail("xingyizhe@qq.com");
//模拟线程二
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user2.setName("zhangsan4444");
user2.setEmail("xingyizhe@qq.com");
userMapper.updateById(user2);
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
**性能分析插件
MyBatisPlus提供性能分析插件,如果超过这个时间就停止运行
条件构造器
复杂的SQL语句用Warpper来替代条件
1.测试不为空的情况
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();创建querywrapper对象类似于HashMap,采用链式结构
@Test
void contextLoads() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.isNotNull("name")
.isNotNull("email")
.ge("age",20);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
更多条件查看:
